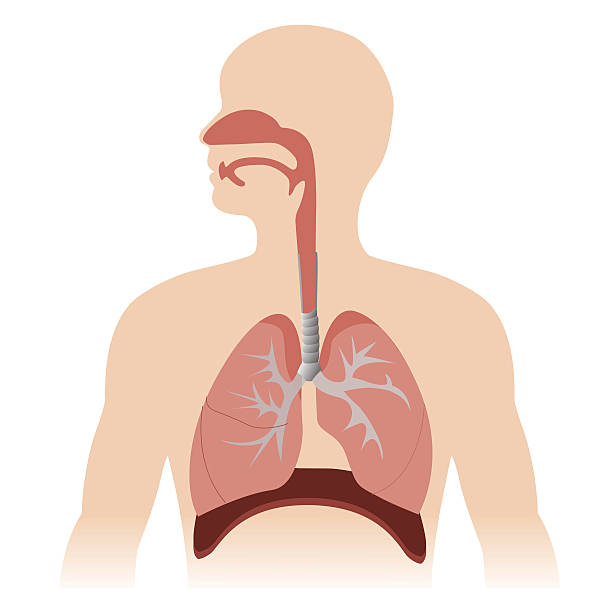
human respiratory system anatomy. vector format illustration.
Browse 790+ gaseous exchange illustrations stock illustrations and vector graphics available royalty-free, or start a new search to explore more great stock images and vector art.

human respiratory system anatomy. vector format illustration.
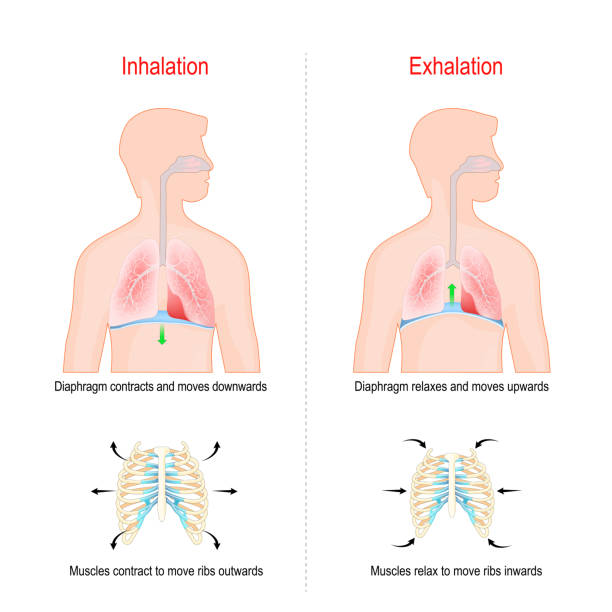
Cycle of breathing, inspiration and expiration. Role of Diaphragm and intercostal muscles (ribs and chest) in Gas exchange in lungs. respiratory system anatomy. vector illustration
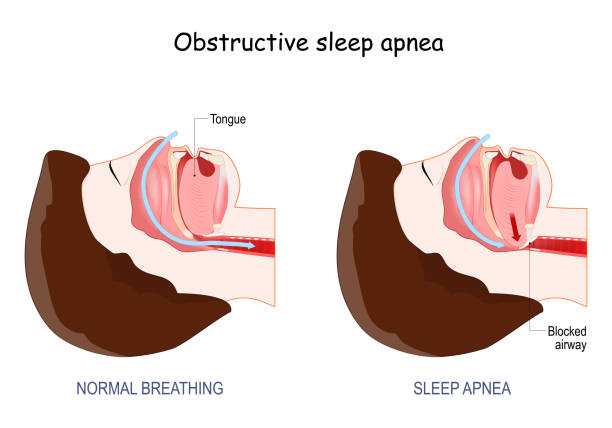
Obstructive Sleep Apnea. normal breathing, and anatomy of Snoring. Cross section of human's head. Blocked airway with Tongue.

Lung Tissue Engineering in Regenerative Medicine and Pneumology - Development of Lung Replacement Devices and Tissues to Treat Patients with Lung Disease - Conceptual Illustration
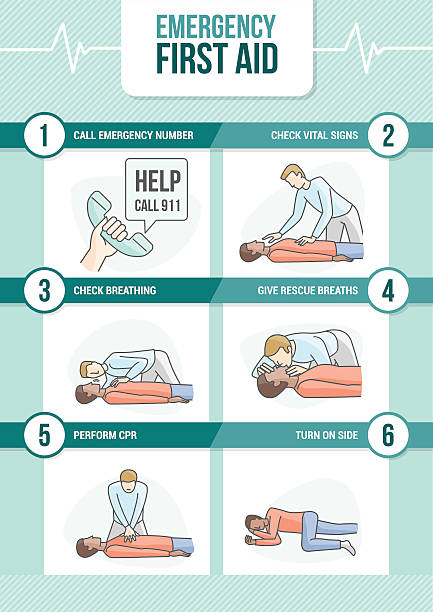
Emergency first aid cpr procedure with stick figures giving rescue breath and cardiomanipulatory resuscitation

Cardiopulmonary resuscitation, cpr reanimation and first aid procedures step by step. Health help, emergency training. Cardiac massage vector concept. Illustration of cardiopulmonary reanimation
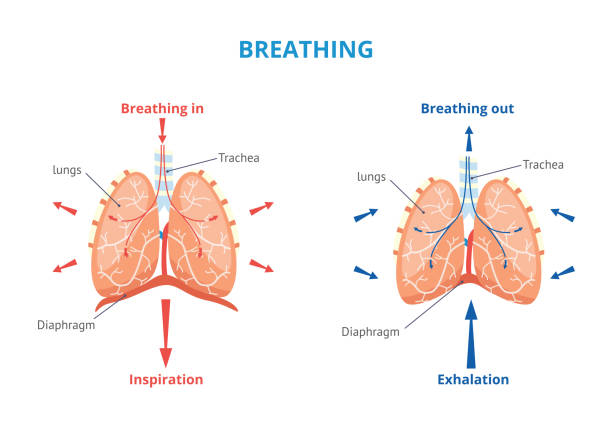
Respiratory system of human depicting breathing in and out airway vector medical banner or placard illustration with inscriptions. Anatomy and physiology educational diagram.
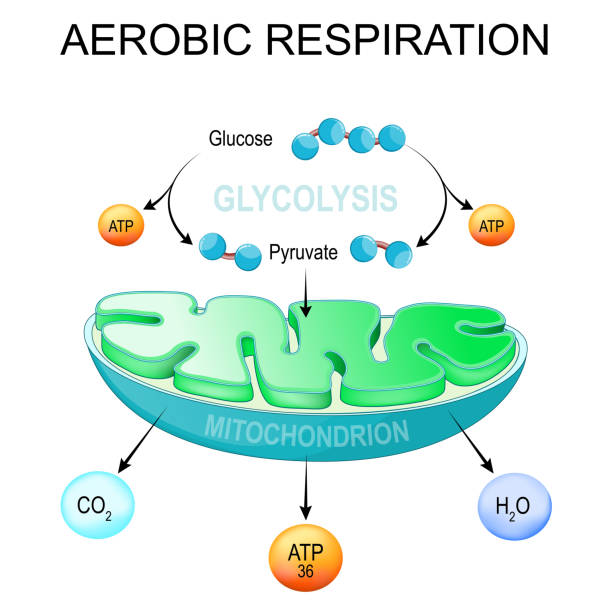
aerobic respiration. Glycolysis and ATP Synthesis in mitochondria. converting glucose into pyruvate in cells. metabolic pathway. Vector poster
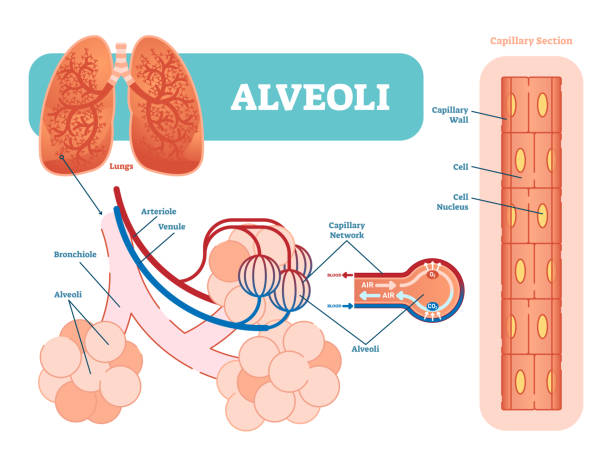
Lungs alveoli schematic, anatomical vector illustration diagram with capillary network. Medical information poster.

Snoring vector illustration. Young man lying in the bed, snores loudly with open mouth while deep sleep. Male person catching some zzz's. Sleep apnea, snoring, fast asleep concept for web.Flat design
Human lungs showing breathing concept.

Pleural effusion disease. Fluid between the layers of tissue in lungs and chest cavity. DIfficult breathing. Unhealthy internal organs in the human body. Respiratory system medical vector illustration
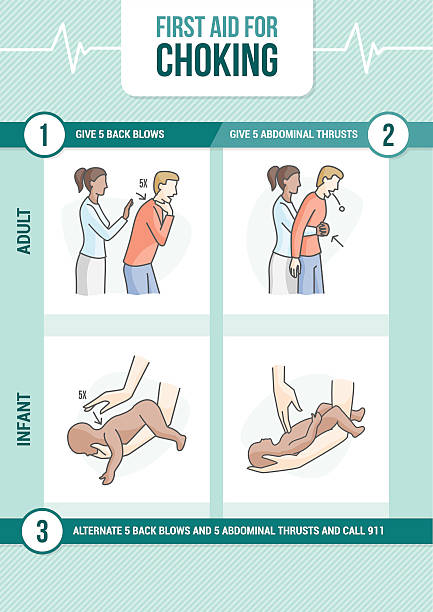
First aid procedure for choking and heimlich maneuver for adults and infants

Human nose sensing, smelling or inhaling a smell or substance.
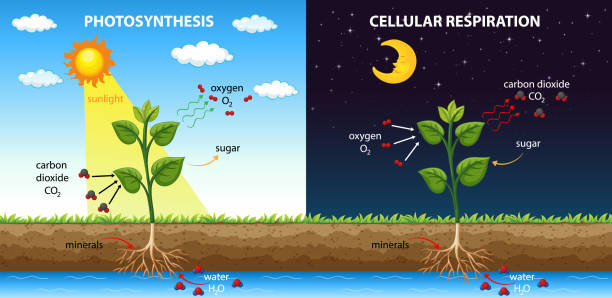
Diagram showing cellular respiration and photosynthesis illustration
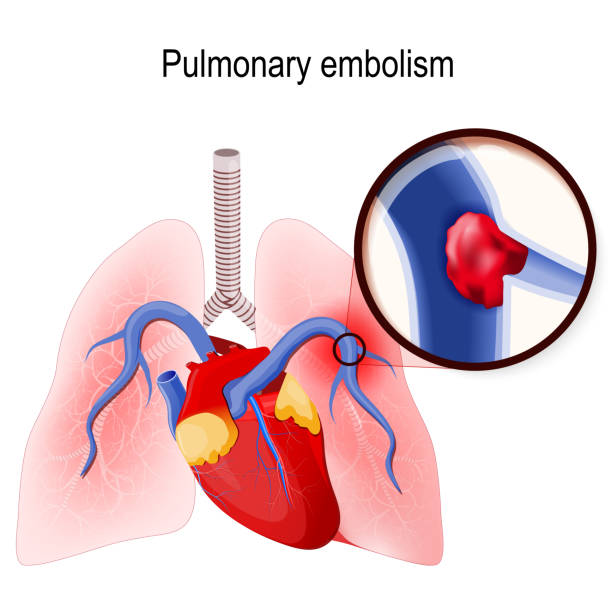
Pulmonary embolism. Blockage of the main artery of the lung or one of its branches by a blood clot that has travelled from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream. Human lungs and heart. blood clot in the vein (close up)

Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products.
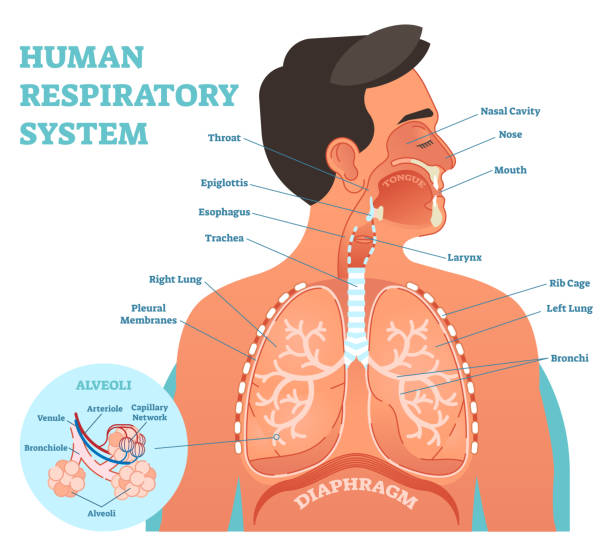
Human Respiratory System anatomical vector illustration, medical education cross section diagram with nasal cavity, throat, esophagus, trachea, lungs and alveoli.
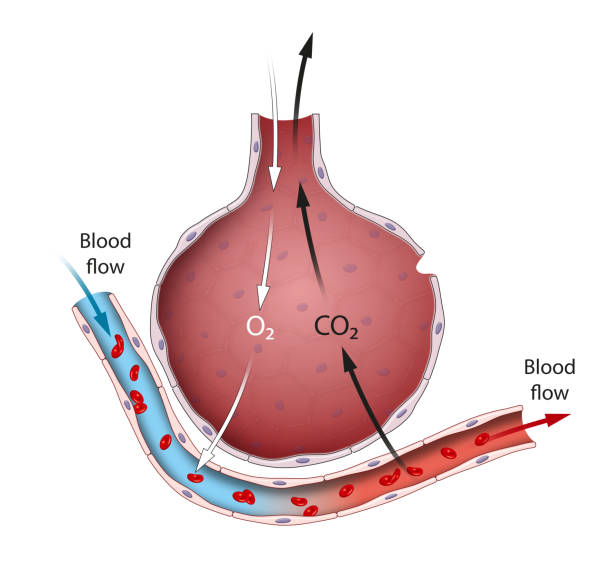
Alveoli are an important part of the respiratory system whose function it is to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules to and from the bloodstream

Human lungs showing pulmonary embolism concept.
Set of human organs and systems of the body vitality. Vector illustration
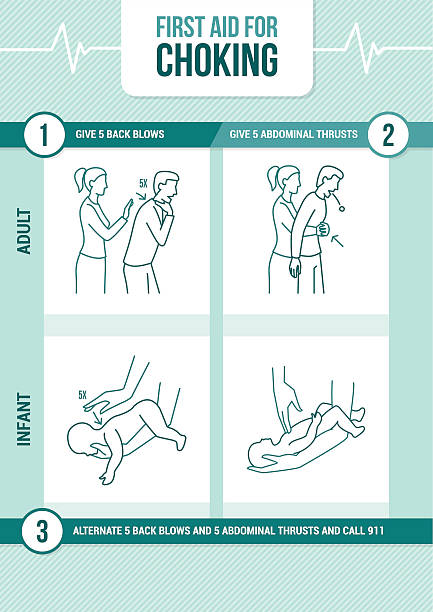
First aid procedure for choking and heimlich maneuver for adults and infants
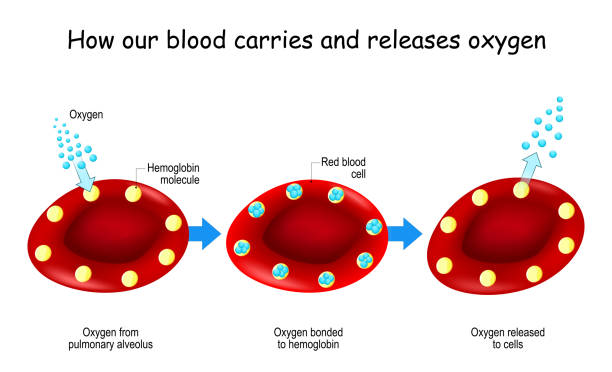
Oxygen and Hemoglobin. How our blood carries and releases oxygen. Red blood cells with hemoglobin molecule. concept Poster about Oxygen transport. Vector Illustration for Science, education, human anatomy, and medical use.

Mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles (mitochondrion, singular) that generate most of the chemical energy needed to power the cell's biochemical reactions. Chemical energy produced by the mitochondria is stored in a small molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP)

Snoring vector illustration. Woman lying in the bed, snores loudly with open mouth while deep sleep. Female person catching some zzz's. Sleep apnea, snoring, fast asleep concept for web.Flat design

Oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange in lungs and alveolus. Detailed illustration isolated on white background. Cartoon style

Pulmonary hypertension is an increased blood pressure within the arteries of the lungs. Cross section of the Normal, and narrowing of blood vessels. Humans heart with hypertrophy of Right ventricle and pulmonic regurgitation

Emergency first aid cpr procedure with stick figures giving rescue breath and cardiomanipulatory resuscitation

human respiratory system anatomy, vector medical nose illustration
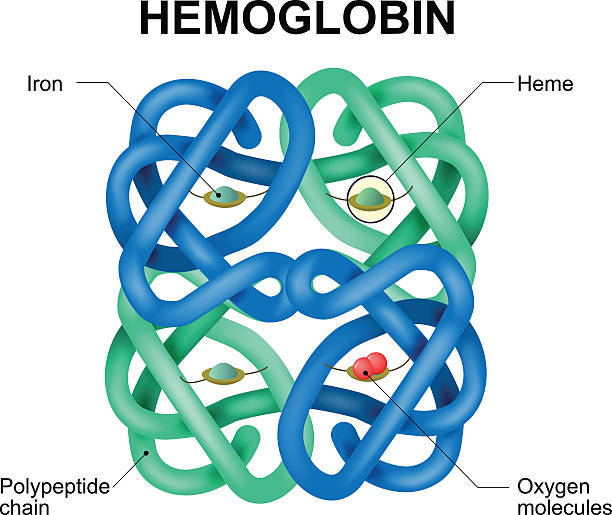
Structure of human hemoglobin molecule. Vector diagram. Hemoglobin is the substance in red blood cells that carries oxygen.

Heimlich maneuver procedure, removal of foreign object from respiratory tract flat style, vector illustration isolated on white background. First aid, helping character, health and medicine
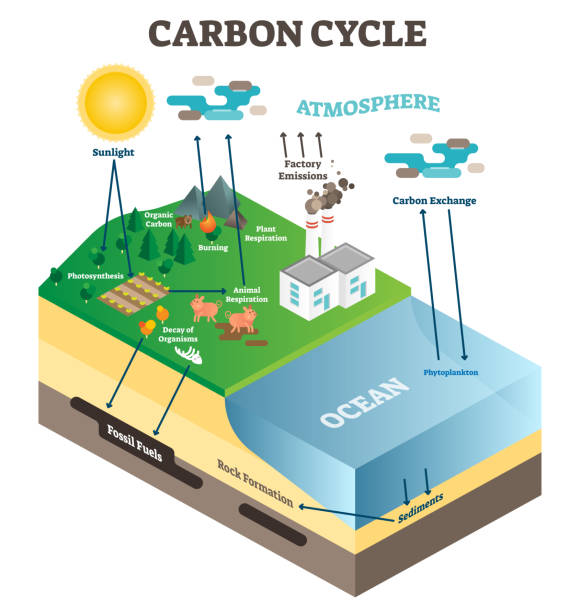
Atmosphere carbon exchange cycle in nature, planet earth ecology science vector illustration diagram scene with ocean, animals, plants and industrial factory. Educational information poster.

Function of mitochondria. Mitochondria convert food energy into energy for biological processes like Inflammation, ATP production, Immunity regulation, Calcium homeostasis, Senescence of cell, Stem cell regulation and Apoptosis. Vector illustration

Team of doctors diagnose respiratory system
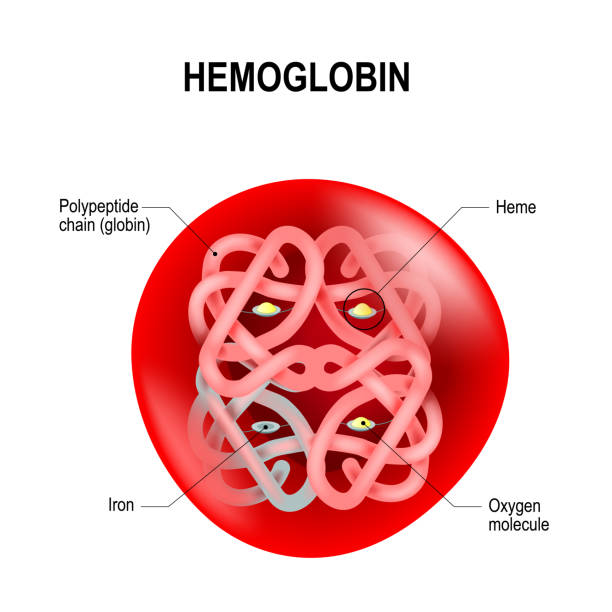
Red blood cell with hemoglobin. Structure of human hemoglobin. schematic visual model of oxygen-binding process. Vector illustration for your design and medical use.

diaphragm functions in breathing. Breath and Exhalation. enlarging the cavity creates suction that draws air into the lungs
Engraved illustrations of Anatomy of the Fasciae, Integuents, and Organs of Mastication and Respiration from Iconographic Encyclopedia of Science, Literature and Art, Published in 1851. Copyright has expired on this artwork. Digitally restored.

ATP ADP cycle. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a organic chemical that provides energy for cell. intracellular energy transfer. Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) is organic compound for metabolism in cell. Vector diagram for educational, biological, medical and science use. model of molecule adenosine triphosphate, and Adenosine diphosphate
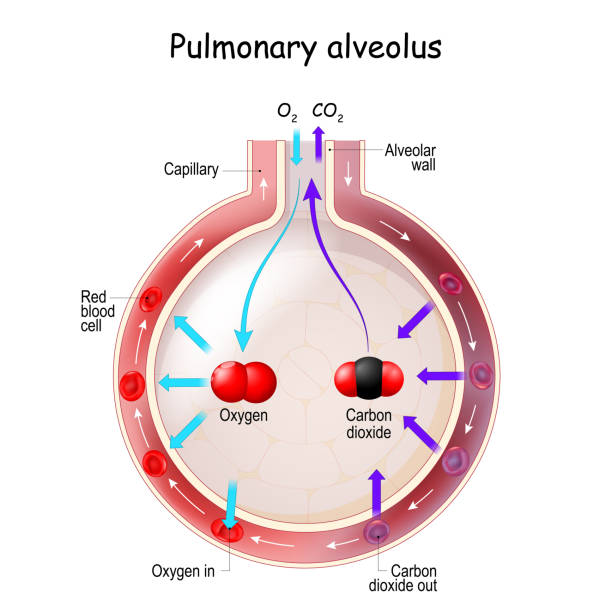
Alveolus Gas Exchange. Anatomy of Pulmonary alveolus. Oxygen And Carbon Dioxide, inhale and exhale
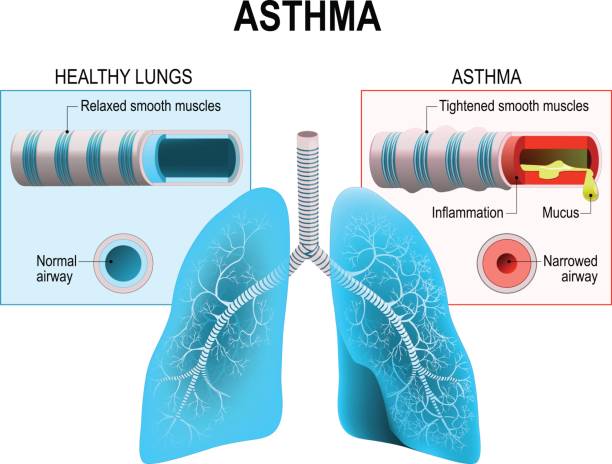
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways that is characterized by narrowing of the airways bronchospasm and coughing. Humans lungs and bronchi
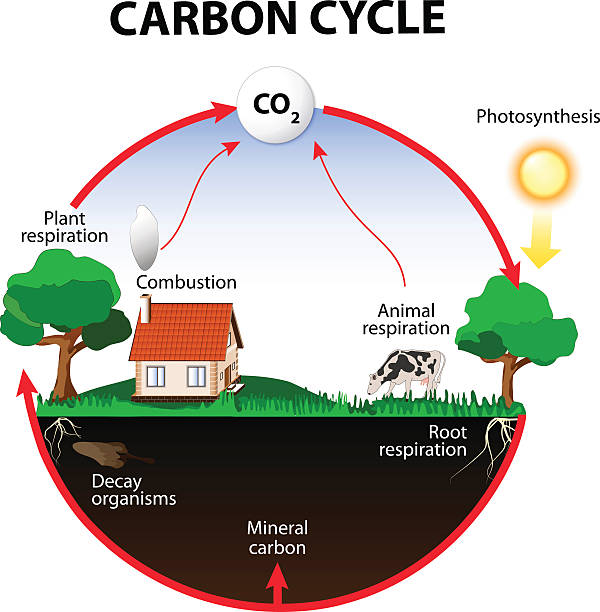
carbon cycle. The carbon path from the atmosphere, into living organisms, then turning into dead organic matter, and back into the atmosphere.

Legionnaires disease or legionellosis or Legion fever. Signs and symptoms is a form of atypical pneumonia. Human silhouette with highlighted internal organs

Collapsed lung. abnormal collection of air (pneumothorax) or fluid (pleural effusion) or pus (empyema) in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall.

People in chemical protection suit stops the virus. Coronavirus 2019-nCoV. stock illustration

Pulmonary edema, lung problem vector illustration diagram with bronchi and fluid leakage in alveoli. Chest cross section human body scheme. Health care information.

Painful throat concept vector illustration with coughing human torso. Graphic symbol pain circles on neck. Cold virus health problems.

Pulmonary alveoli. gas exchange in a lungs. Respiratory bronchioles with Alveolar sacs. Cross section of the alveolus and capillary. Respiratory system. Vector illustration
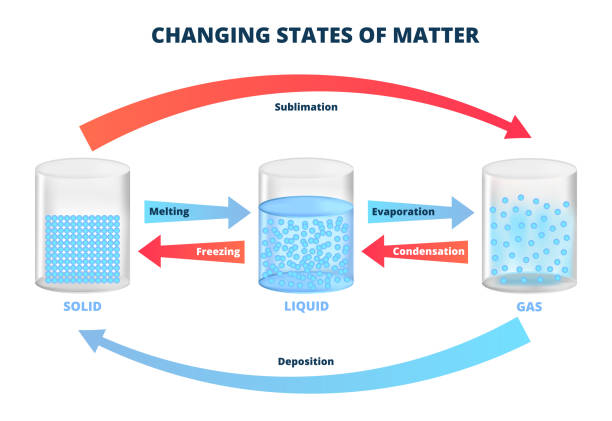
Vector diagram with changing states of matter, three states of matter with different molecular arrangements – solid, liquid, gas. Scientific or chemical infographic isolated on a white background. Freezing, melting, condensation, evaporation, sublimation, deposition.
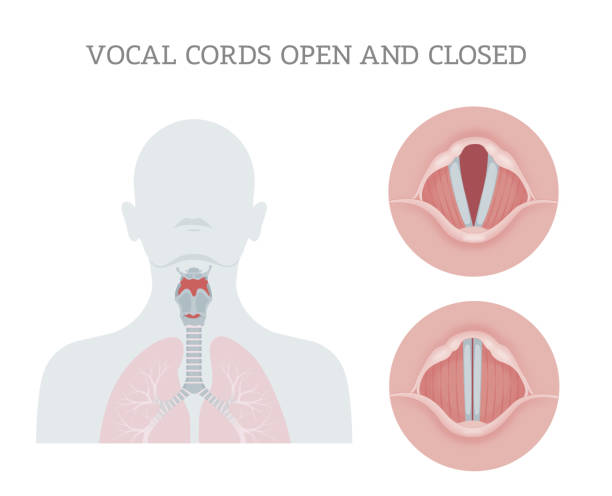
Vocal cords are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through vocalization. The size of vocal cords affects the pitch of voice. They are composed of twin infoldings of mucous membrane stretched horizontally, from back to front, across the larynx. They vibrate, modulating the flow of air being expelled from the lungs during phonation
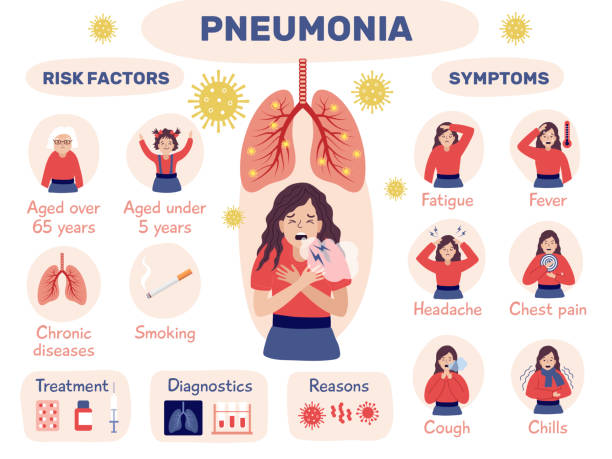
Pneumonia infographic. Health problem with lung bacterias attack human organs recent vector illustrations of infographic respiratory illness

Half section of a mitochondrion isolated on white

Human Body Anatomy. Body systems. Skeletal and muscular, nervous ans circulatory, lymphatic and digestive systems. Vector ilustration

Doctor and nurse care for patients in the intensive care unit. Thank you nurses and doctors. Medical technology and life saving. vector illustration.
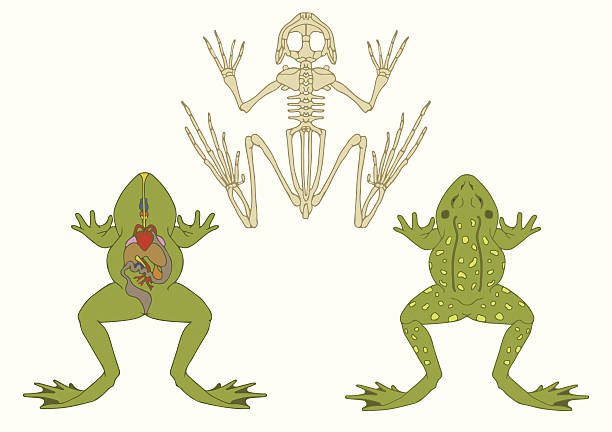
zoology, anatomy of amphibian, cross-section and skeleton
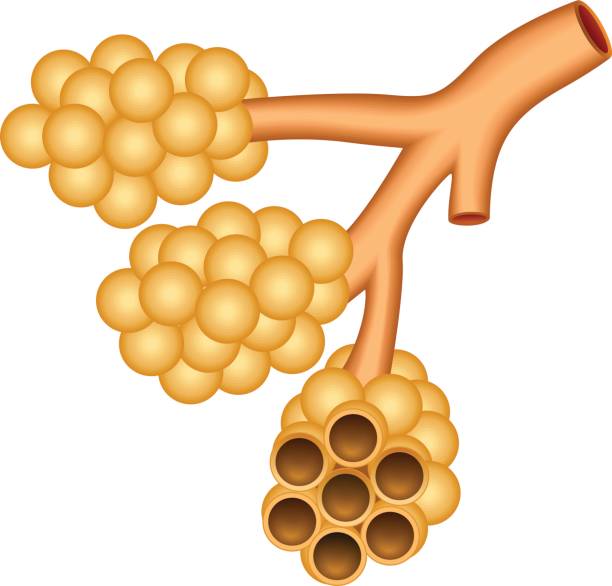
Pulmonary Alveoli in Vector image.
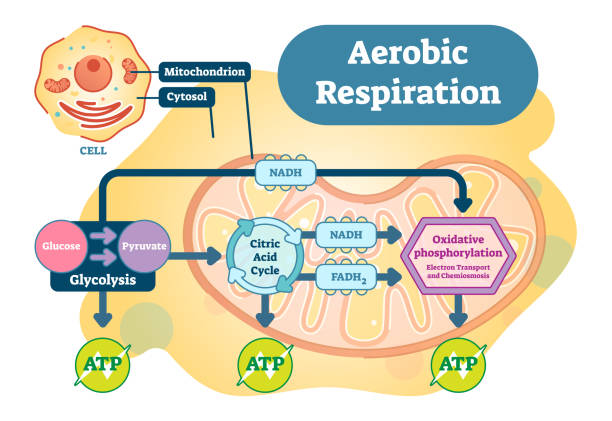
Aerobic Respiration bio anatomical vector illustration diagram, educational medical scheme.